







In Greek mythology, Pollux and Castor were the sons of King Tyndareus of Sparta and his wife Queen Leda. The constellation Cygnus represents the swan Zeus transformed himself into on his adulterous visit to Leda, and of the twins, Pollux was the son of Zeus, whereas Castor was the son of Leda’s husband, and was therefore mortal. Throughout their lives the twins were inseparable and had many legendary adventures together, including joining Jason and the Argonauts on their quest for the Golden Fleece. Eventually Castor died and Pollux, unable to be parted from his brother, asked Zeus to make him mortal too. Zeus refused but when Pollux followed his brother into the underworld, Zeus was so impressed by his devotion that he granted him the request on the condition that each could only spend half of the year on Olympus; the other half was to be spent in the Underworld. Zeus also moved them both into the heavens as the constellation Gemini.
Mythology

Gemini
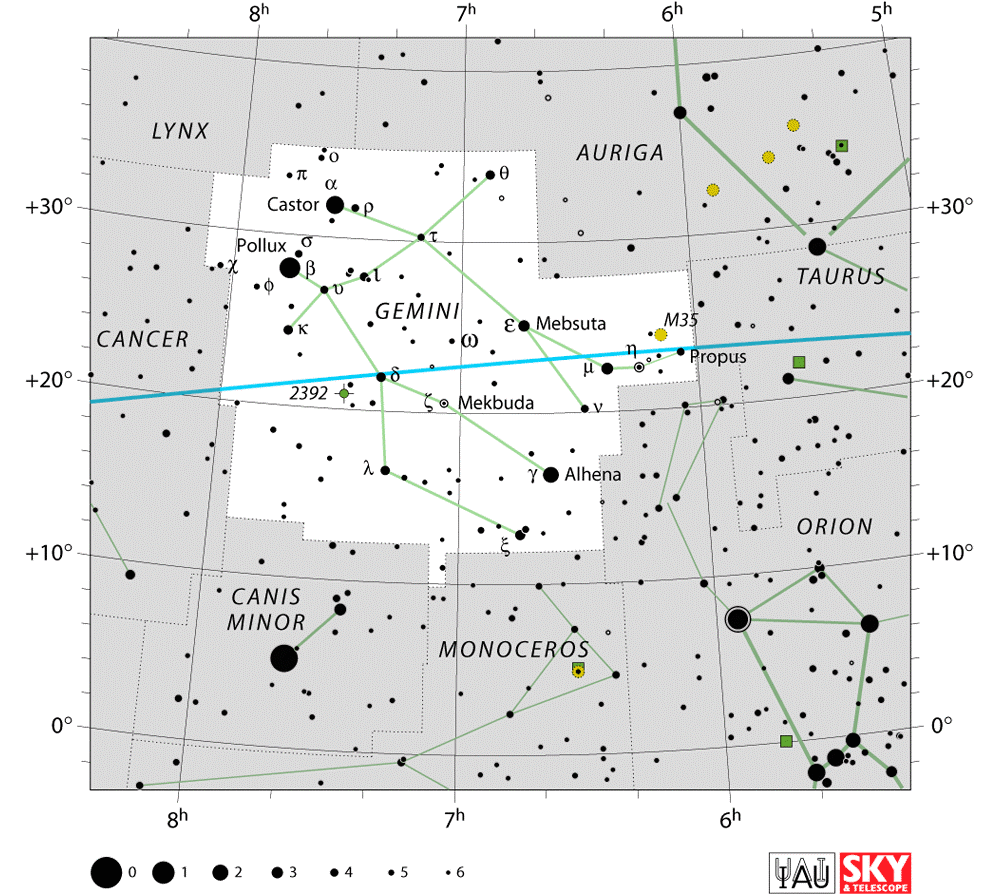
Gemini is Latin for "twins," and it is one of the few constellations that actually looks like its namesake. Gemini is one of the Zodiac constellations and one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy.
Location

Gemini is fairly easy to spot in the sky, even for amateur star gazers. It is located northeast of Orion, and between Taurus and Cancer on the elliptic.
-
Right ascension: 7 hours
-
Declination: 20 degrees
-
Visible between latitudes 90 and minus 60 degrees
-
Best viewing is during February. By April and May, the constellation can be seen soon after sunset in the west.
Deep Sky Objects in Gemini
Messier 35 (NGC 2168)
-
Messier 35 is an open star cluster in Gemini. It covers an area of the sky as big as the full Moon.The cluster has an apparent magnitude of 5.30 and is approximately 2,800 light years distant from Earth.
NGC 2158
-
NGC 2158 is another open cluster in Gemini. It lies to the southwest of Messier 35. The cluster has an apparent magnitude of 8.6 and is approximately 11,000 light years distant from the Sun. It is believed to be about a billion years old.

Eskimo Nebula (NGC 2392, Caldwell 39)
-
is a spectacular planetary nebula, and the first object photographed by the Hubble Space Telescope after a successful servicing mission in 1999. It is a bi-polar, double-shell nebula with the remains of the progenitor star clearly visible near the center of the structure. The name “Eskimo Nebula” derives from the fact that the nebula resembles a face enclosed by a fur-collared parka. The Eskimo Nebula lies about 2,870 light years away, and with an apparent visual magnitude of 10.1, is an easy target even for modest amateur equipment in dark skies.
Jellyfish Nebula – IC 443 (Sharpless 248)
-
IC 443 is a Galactic supernova remnant in Gemini.
-
The nebula is approximately 5,000 light years from Earth.
-
It can be found near the bright star Eta Geminorum.
-
It is also known as the Jellyfish Nebula.
-
The Jellyfish Nebula is believed to be a remnant of a supernova that occurred 3,000-30,000 years ago.
-
It is about 70 light years in size.
-
The supernova explosion that resulted in the creation of the nebula also created a neutron star, and it is believed to have been a Type II supernova, a violent explosion of a massive progenitor star.

Geminga
-
Geminga is a neutron star in the Gemini constellation, a decaying core of an old massive star that ended its life in a supernova explosion about 300,000 years ago. Its name is derived from the Italian gh’è minga, which means “it’s not there,” and at the same time it is short for “Gemini gamma-ray source.” The star has an apparent magnitude of 25.5 and is approximately 815 light years distant from the Sun.
The Geminids
-
is the most prolific meteor shower of the year, and runs from December 4th to 17th, with a peak on the 13th/14th when 120–160 meteors per hour can be seen . The Geminids are visible from all over the globe, and are a slow meteor shower, which have the ability to penetrate deep and burn up low in the Earth’s atmosphere. As a result, beautiful long arcs are created across the night sky, many lasting a second or two. Unlike most other meteor showers that originate from cometary debris, the Geminids are associated with the asteroid 3200 Phaeton.
The Rho Geminids
-
is a singularly unspectacular meteor shower that runs from December 28th to January 28th, with a maximum of fewer than 8 meteors per hour on the peak that falls on January 8th.